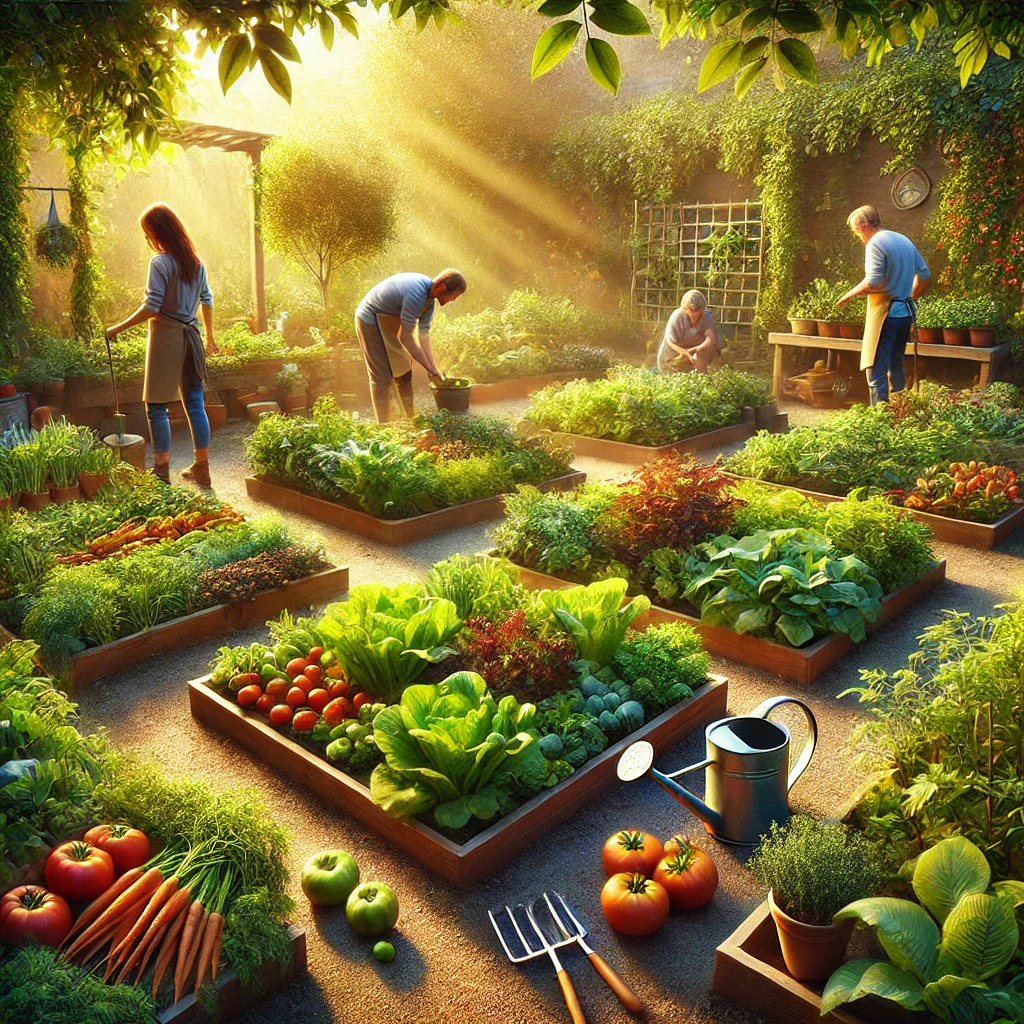
Tips for Cultivating a Healthy Garden
 Healthy Garden
Healthy Garden
Creating and maintaining a healthy garden is both an art and a science. Whether you are a novice gardener or an experienced green thumb, a few key practices can ensure your garden thrives. Below are practical tips to help you cultivate a lush, vibrant, and productive garden.
1. Start with Quality Soil
Healthy soil is the foundation of a successful garden. Conduct a soil test to determine its pH and nutrient levels. Most plants thrive in soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.5. Amend your soil with organic matter such as compost, aged manure, or peat moss to improve its texture, fertility, and water retention.
2. Choose the Right Plants for Your Region
Selecting plants suited to your climate and soil conditions minimizes stress on your garden and increases the likelihood of success. Check the USDA Hardiness Zone map or consult local nurseries to identify plants that will thrive in your area.
3. Plan for Proper Sunlight
Understand your garden’s light conditions. Some plants, like tomatoes and roses, require full sun (6–8 hours of direct sunlight daily), while others, like ferns and hostas, prefer partial or full shade. Position your plants accordingly for optimal growth.
4. Water Wisely
Water is essential, but how and when you water can significantly impact plant health. Water deeply and less frequently to encourage deep root growth. Early morning is the best time to water, as this reduces evaporation and gives plants time to dry before night, preventing fungal diseases.
5. Practice Companion Planting
Pairing compatible plants can boost growth, deter pests, and enhance the garden’s health. For example, marigolds deter nematodes, and planting basil near tomatoes can enhance flavor and repel insects.
6. Manage Pests Naturally
Prevent pests without harmful chemicals by encouraging natural predators such as ladybugs and birds. Use physical barriers like row covers or employ organic solutions like neem oil and insecticidal soaps. Handpicking pests or using traps is another effective method.
7. Regular Pruning and Maintenance
Pruning promotes healthy growth, improves airflow, and reduces the risk of disease. Remove dead or diseased branches promptly and regularly deadhead flowers to encourage new blooms.
8. Rotate Crops
If you grow vegetables, avoid planting the same crops in the same spot year after year. Crop rotation prevents nutrient depletion and reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases.
9. Mulch to Retain Moisture and Suppress Weeds
Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips, straw, or grass clippings, around plants. Mulch conserves moisture, regulates soil temperature, and minimizes weed growth.
10. Fertilize Responsibly
Feed your plants with a balanced fertilizer tailored to their needs. Organic options, like compost tea or fish emulsion, provide nutrients while being environmentally friendly. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to weak growth and environmental harm.
11. Encourage Biodiversity
A garden with a variety of plants is less susceptible to pests and diseases. Mix flowers, vegetables, and herbs to attract beneficial insects and pollinators like bees and butterflies.
12. Monitor and Adjust
Gardening is an ongoing process. Regularly check your plants for signs of stress, pests, or disease. Be willing to adjust your care routine based on the seasons and changing conditions.
Conclusion
Cultivating a healthy garden requires attention, patience, and consistent care. By focusing on soil health, plant selection, and sustainable practices, you can create a thriving garden that brings beauty and bounty year-round. Gardening not only enhances your outdoor space but also provides a rewarding connection to nature. Start small, stay persistent, and watch your garden flourish.
Happy gardening!
Share this content:




















Post Comment